Iron pipes have been a cornerstone of modern infrastructure for centuries, used for everything from water supply systems to industrial applications. Two major types of iron pipes commonly used in construction and piping systems are ductile iron and cast iron. While both materials are made from iron, their properties, manufacturing processes, and suitability for various applications differ significantly. In this article, we will delve deep into the key differences between ductile iron and cast iron pipes, highlighting their individual benefits and how they affect their real-world applications.
What is Cast Iron?
Cast iron is a group of iron-carbon alloys with a carbon content greater than 2%. It is typically produced by melting iron and pouring it into molds to cool and solidify. The resulting material has excellent castability, durability, and is relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for various piping and structural applications.
Properties of Cast Iron:
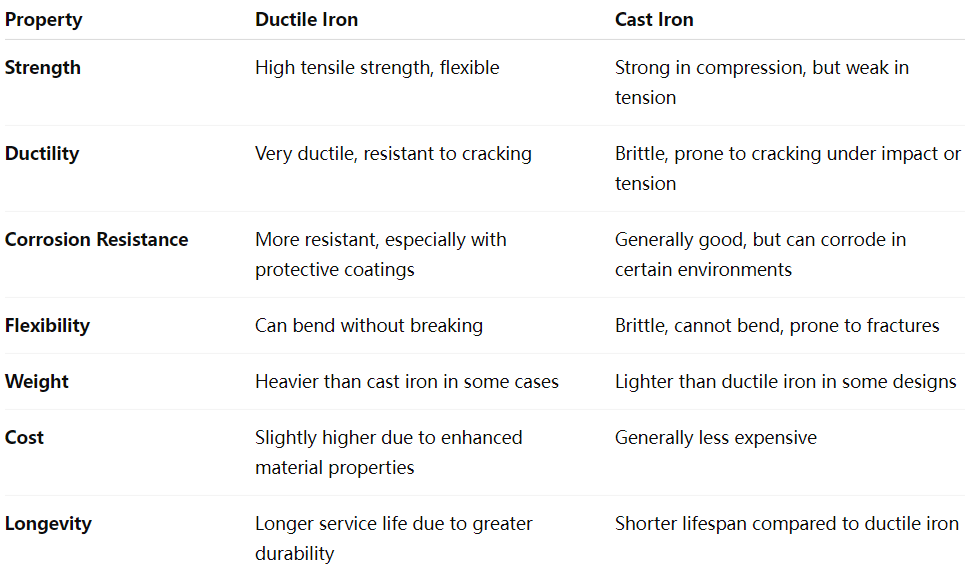
Brittleness: Cast iron is hard but brittle. It is prone to cracking and breaking under tension or impact.
Strength: Cast iron pipes are strong in compression, but weaker in tension and bending.
Corrosion Resistance: Cast iron has good resistance to corrosion, though it can deteriorate over time, especially in acidic or moist environments.
Manufacturing: The casting process gives cast iron pipes a smooth inner surface, which helps in the flow of liquids.
Historical Use: Cast iron pipes were widely used for water, sewer, and gas lines from the 19th century up until the mid-20th century.
What is Ductile Iron?
Ductile iron, also known as nodular cast iron or spheroidal graphite iron, is an enhanced form of cast iron. Its primary difference lies in its composition: ductile iron contains small amounts of alloying elements, like magnesium, which alter the structure of the graphite in the material. This modification results in a more ductile, or flexible, material as compared to regular cast iron.
Properties of Ductile Iron:
Ductility: Ductile iron is much more flexible than cast iron, meaning it can bend or stretch without breaking. This flexibility makes it less likely to crack under stress.
Strength: Ductile iron has superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to cast iron, making it more durable in challenging environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Similar to cast iron, ductile iron is resistant to corrosion but is typically more resilient when exposed to corrosive conditions, thanks to improvements in its composition and manufacturing.
Manufacturing: Like cast iron, ductile iron pipes are created using a casting process, but the addition of magnesium allows for a more malleable material.
Modern Use: Ductile iron pipes have largely replaced cast iron in most modern water, wastewater, and industrial piping systems due to their enhanced properties and durability.
Key Differences Between Ductile Iron and Cast Iron Pipes
While both materials are iron alloys, the differences between ductile and cast iron pipes can greatly affect their performance and suitability for different applications.
Advantages of Ductile Iron Over Cast Iron
Higher Durability:
Ductile iron pipes have a longer lifespan and are less likely to crack, break, or degrade under harsh conditions. This makes them ideal for high-pressure systems and areas prone to seismic activity.
Improved Flexibility:
Ductile iron’s flexibility allows it to absorb shocks and resist fractures, a major advantage over the brittle nature of cast iron. This is particularly valuable in applications where movement or shifting of the ground could occur, such as earthquake-prone regions.
Superior Corrosion Resistance:
Though both materials offer good corrosion resistance, ductile iron tends to last longer in aggressive environments like moist soil, where cast iron may corrode more rapidly. The increased strength and tougher surface also allow ductile iron pipes to better withstand water treatment chemicals.
Ease of Installation:
Due to its ductility, ductile iron pipes can be installed with fewer risks of breakage during transportation or installation. This reduces labor costs and the risk of damage in the field.
Versatility:
Ductile iron is suitable for a wider variety of applications, from potable water systems to industrial wastewater systems and even gas pipelines, whereas cast iron is mainly used in lower-pressure systems and older infrastructure.
Applications of Ductile Iron vs Cast Iron Pipes
Ductile Iron Pipes are used for a variety of applications, including:
Water distribution: Ductile iron is the preferred choice for modern potable water and sewage systems due to its strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance.
Sewerage systems: They are commonly used for wastewater management, especially in areas with seismic activity or unstable soil conditions.
Gas pipelines: Ductile iron can handle high-pressure gas systems safely and reliably.
Industrial applications: Often used for industrial wastewater systems and oil pipelines, where durability and resistance to corrosion are key requirements.
Cast Iron Pipes, on the other hand, are more commonly found in older infrastructure, such as:
Sewer systems: Cast iron was widely used in sewer systems until it was largely replaced by ductile iron.
Historical water systems: Many historical buildings and cities still have cast iron water pipes, though these are increasingly being upgraded or replaced due to their vulnerability to corrosion and breakage.
Conclusion: Which is Better? Ductile or Cast Iron Pipes?
While both ductile iron and cast iron have their uses, ductile iron is generally the superior choice for modern applications due to its enhanced flexibility, strength, and durability. As infrastructure demands evolve and systems require increased reliability and longer lifespans, ductile iron pipes continue to gain preference across the globe. Cast iron pipes, while still functional and cost-effective in certain situations, are increasingly being phased out in favor of their more advanced counterpart.
Ultimately, the choice between ductile iron and cast iron pipes depends on the specific needs of the application, budget, and expected lifespan of the installation. However, for most modern installations and critical infrastructure, ductile iron is the material of choice.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English русский
русский






